Table of Contents
ToggleFull stack testing is a comprehensive approach to thoroughly test any application’s user interface (UI) along with the server-side logic. Full stack testing helps check every application component, like finding any non-functioning feature in the front end or flaws in the back end.
A Consortium for Information & Software Quality (CISQ) study found that poor software quality costs in U.S. businesses rose to at least $2.41 trillion. The rise in cybercrime losses also increased gradually due to increasing vulnerabilities. This is where full-stack testing helps us to get info about how modern applications are built with multiple interconnected layers, databases, and interfaces, making it essential to ensure everything works together seamlessly.
For those who want to master this in-demand skill, STAD Solutions offers a software testing course. This course will help you get started with full-stack Testing and provide hands-on experience that will help you get placed in high-paying organizations.
What is Full Stack Testing?
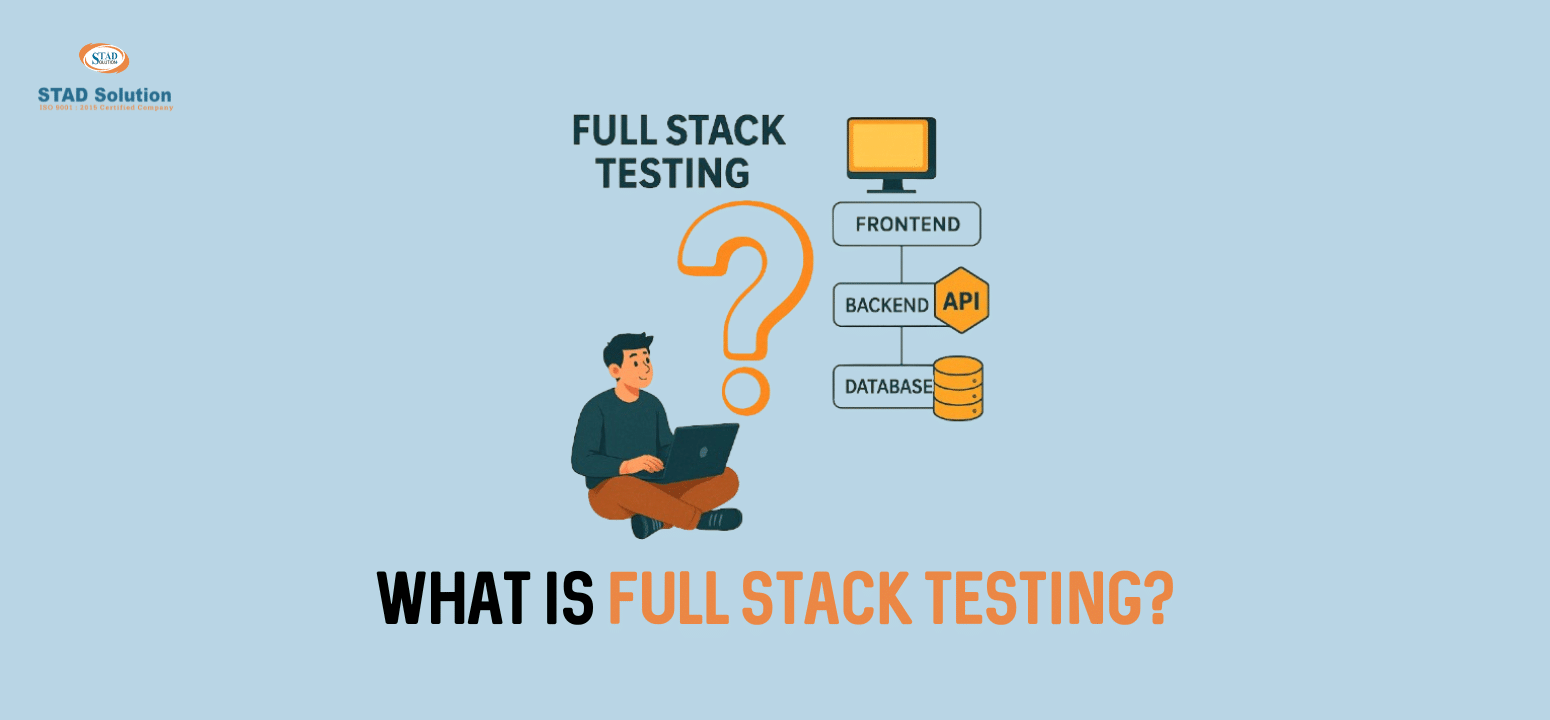
Full stack testing is a methodology meant to provide different testing environments, involving checks at every possible layer of a particular application by ensuring that everything is working coherently. This can be seen as a typical testing path that depends upon the parts of an application, such as unit testing for smaller snippets of code, UI testing for front-end tests, etc., but full-stack testing tends to scope everything.
- Front-end: The end-user layer, from buttons to forms to layouts-and all other interactive features created with the use of technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Back-end: The server-side layer, including APIs, business logics, and procedures that generally take care of data management as well as application performance using software programming languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js.
- Database: The storage layer concerned with managing, retrieving, and updating the data, using commonly MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
Why Full Stack Testing is Important
Today’s customers demand lightning-fast applications which can work seamlessly and intuitively. A single failure, such as a crashed checkout process on a missing database entry, drives the users mad, thus tarnishing the image of a company.
- Improving Integration Hostility Reduction: According to a study under IEEE Software conducted in 2023, 70% of software defects occurred due to integration between different layers, as verified by their sources. And catching integration-related issues during end-to-end full-stack testing minimizes the amount of rework required.
- Increased User Satisfaction: According to Fairfield, Connecticut, 89% of users will abandon an application if it does not perform well or has bugs (source), and full-stack testing makes sure there is a seamless experience across all layers.
- Reducing Expenses: The cost estimates provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), defect corrections after release could be 30 times more expensive than during development. Full stack testing would facilitate detection in early stages and consequently save huge costs.
- Drives Market Growth: The worldwide market for software testing is expected to cross the $70 billion mark by the year 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5%. In 2023, it was valued at $51.8 billion and is propelled by the demand for strong testing, like full-stack testing (source).
How Does Full Stack Testing Work?
It starts with unit testing; thus, every function is verified, covering each and every aspect and failing all checks.
Component Testing
- Tests a single entity, like a specific function or module, to verify whether it works properly while isolated from everything else. It confines one specific component to demonstrate whether it works in isolation.
- Example: The Login function must be tested to check proper validation of credentials.
- Tools: JUnit (back-end), Jasmine (front-end).
Integration Testing:
- Concerns different components, such as front-end and back-end, but their interaction is expected.
- Example: The form submission will end with updating data in the database through an API call.
- Tools: Postman (API testing) & Selenium (UI-API integration).
System Testing:
- Will test the system as a whole against its requirements and ensure that it meets both functional (e.g., features) and nonfunctional (e.g., performance) specifications.
- Tools: TestRail (test case management).
End-to-End Testing:
- This test mimics real-world user scenarios to test how the application performs for a real user.
- Example: Registering.
Benefits of Full Stack Testing
Through full-stack testing, overall software quality is enhanced, and development is improved. Here are the key advantages:
- Early Integration Problem Detection
- Bugs are commonly manifested when disparate layers fail to communicate with each other.
- Full stack testing is capable of catching this issue early, so that it takes less time to troubleshoot.
- User Experience Improvement
- Validating the entire stack provides full stack testing with an assurance of a seamless, user-friendly application that satisfies its customers.
- Cost Reduction
- Fixing issues during the normal course of development is much cheaper than fixing them after the product has been shipped. Full stack testing will check for many humble yet important issues that may allow one to reduce the post-release fixing costs.
- Greater Reliability
- Applications that have been tested across all layers are stable projects that meet real-life performance, thus creating trust and easier acceptance.
Studies show that over 70% of defects in software arise out of integration failures-which are exactly the integration issues that full stack testing is trying to catch.
Full Stacks Testing Tools in 2025
Effective full-stack testing is made possible with an entire set of specialized full-stack testing tools intended for each layer of an application. Here is a summary of some famous tools and their applications:
| Layer | Tools | Purpose |
| Execution | Selenium, Cypress | Automates UI testing across browsers |
| Back-end | Postman, JUnit | Test APIs and server-side logic |
| Database | SQLUnit, DBFit | Validates data operations |
| End-to-End | TestCafe, Playwright | Simulates full user journeys |
Some primary features of these tools are:
- Selenium: Widely used to automate browser interactions, Selenium is also one of the best tools to test the front-end functionality of applications across many platforms.
- Postman: Most powerful API testing tool. It has an easy interface for back-end validation.
- Cypress: Cypress is a tool that works fast and provides you with live feedback, and is best for front-end and end-to-end testing.
- TestCafe: An end-to-end testing tool that runs in all browsers without plugins.
How to Get Started with Full Stack Testing
Here is a step-by-step guide that anyone can use to get started with full-stack testing.
- Understand the Basics: Know the structure of applications, like the front end, back end, and database, and how they interact.
- Master Key Tools: Get your hands dirty with the full stack testing tools such as Selenium, Postman, and Cypress.
- Practice in Real-Time: Put the theory into practice – probably the best way to learn. Experiment with small applications or even contribute to open-source projects for skill development.
- Learn Automation: Automate repetitive tasks by scripting them for efficiency and increased accuracy.
- Continuous Learning: Keep abreast with the new tools and trends in the ever-changing field of testing.
Why People Choose Full Stack Testing Training by STAD Solutions?
The difference between simply learning full-stack testing and excelling at it lies in the training. And that’s what STAD Solutions has exactly designed – a whole package of resources and services that are all required. Visit and kick-start the full stack testing journey.
- Software Testing Course: It is basically a full-fledged program which includes the complete track on full stack testing-from the very rudimentary to advanced, using tools, hands-on projects included.
- Placement Support: Students who are enrolled in the course can get additional benefits from the placement support. We guide students in resume preparation and finding jobs.
Full Stack Testing Examples
Through these full-stack testing examples, one can illustrate in real life how it addresses a quality assurance measure for the applications.
Example 1: E-Commerce Checkout Process
- Front-end: A user adds items into their cart, enters some shipping details, and then clicks on “Checkout.”
- Back-end: The server processes payment, updates the order status, and sends an email confirmation.
- Database: It captures the order, adjusts inventory levels, and updates the user’s purchase history.
- End-to-end: All tests are done together. This starts from browsing, searching, and cart management to order confirmation and validating error-free payment.
If the payment fails to update the database, full stack testing catches this the potential loss or frustration for a consumer is avoided.
Example 2: Creation of a Post by a user on Social Media
- Front-end: A user writes a post and clicks “Share.”
- Back-end: The server receives the post, checks for inappropriate content, and processes it.
- Database: The post saving is assigned to the user’s profile.
- End-to-End: The post appears just right on the user’s feed while visible to the user’s followers.
This full-stack testing example perfectly captures data flow from input to output, covering every possible issue where post visibility may be missing or incorrect.
Full Stack Testing Jobs and Career Opportunities
Rising complexity in software systems has caused a huge increase in full-stack testing jobs. Full Stack Testing jobs are ideal for multi-layered testers who can build a top-of-the-line application.
Key Required Skills for Full Stack Testing Jobs
- Tool Expertise: Knowledge of full-stack testing tools such as Selenium, Postman, and TestCafe.
- Technical Skills: Basic knowledge of front-end technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), and back-end technologies. APIs, databases.
- Automation Skills: Ability to create and maintain automated test scripts.
- Analytical Mind: Excellent problem-solving skills to locate and fix issues across the stack.
Job Roles and Opportunities
- QA Engineer
- Test Automation Specialist
- Full Stack Tester
- Software Test Engineer
Full-stack testing jobs in India include both UI and backend testing of software applications to provide a seamless end-user experience along with a well-functioning backend. These jobs usually have a salary range of ₹ 4,00,000 to ₹ 10,00,000, depending on experience, skills, and location. You can visit STAD Solutions and get better placement training, including mock interviews, resume preparation, interview scheduling, and interview preparation tips, which guarantees a 100% placement result.
The future of full-stack testing is very bright, with the emerging trend of Artificial Intelligence, DevOps, and CI/CD pipelines. Gartner predicts that by 2025, AI will automate 80% of repetitive testing tasks, enhancing efficiency. But these types of testing jobs require some human interaction and cannot just be replaced by AI. Automaton makes the work easy, and the one mastering the use of automation can remain ahead of the curve in these trends.
FAQs
Full stack testing is an end-to-end testing approach that comprises testing all possible stacks in an application. This is done to determine whether all of them integrate seamlessly or not.
Learning full-stack testing guarantees quality software as it minimizes software defects and boosts employability in high-demand full-stack testing positions in the tech industry.
The best full-stack testing tools would include Selenium on the front end, Postman on the back end, and TestCafe for end-to-end testing, ensuring complete layer validation.
Yes, full-stack testing can be automated with the aid of tools like Cypress and Playwright, thus speeding up the process and increasing efficiency after proper training in their applications.
Full stack testing needs knowledge in programming (for example, JavaScript), full stack testing tools like Selenium, and database knowledge (like SQL) to carry out proper testing.
Full stack testing looks at the whole application from front-end to database, while unit testing is limited to an individual component, be it a function or a single module.
Full stack testing catches early integration bugs and hence ensures a happier ending user with fewer fixes after release, so states industry research.
A common example of a full-stack test would be checking the e-commerce checkout: front-end (cart UI), back-end (payment API), and database (order storage) working together.
Full stack testing could have excessive complexity concerns across layers, tool overload, etc., but it is fairly addressable with proper training and automation strategies.


